0
/ 10
Using this class definition:
public class Node<E> { //... instance variables public Node(E d, Node<E> n) { this.data = d;...Using this class definition:
public class Node<E> {
//... instance variables
public Node(E d, Node<E> n) {
this.data = d;
this.next = n;
}
public E getData() {return data; }
public void setData(E d) {data = d; }
public Node<E> getNext() {return next; }
public void setNext(Node<E> n) {next = n; }
}
Assume we have built a linked list
with four nodes as shown in the image below. The
head pointer points to the beginning of the list.
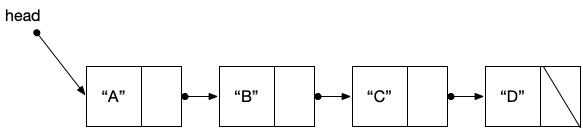
Execute the following lines of code and then select the option below that shows the content of the list after the code executes.
curr = head;
curr = curr.getNext();
curr.setNext(new Node<String>("E", null));
Your feedback will appear here when you check your answer.